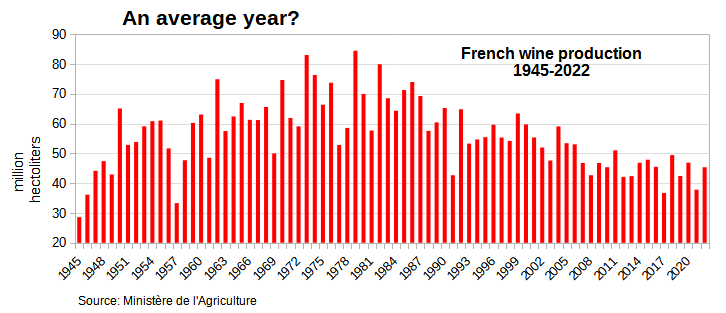
French wine production is currently at a critical juncture, facing significant challenges that threaten its future. The combined effects of climate change have been devastating, leading to a consistent decline in yields and an alarming comparison to the disastrous 2024 harvest. With the 2025 wine harvest on the horizon, many are left wondering if conditions will improve or if another year of scarcity awaits. French winegrowers are also grappling with economic pressures and growing dissatisfaction, culminating in protests against the government’s inadequate support. As the industry navigates these turbulent waters, understanding the impact of climate change and the urgent need for innovation becomes paramount.
The viticulture sector in France is undergoing a transformative period, as producers strive to adapt to the demands of a changing climate and market realities. Wine cultivation, an integral part of the French economy and culture, is confronted by persistent issues impacting grape quality and quantity. As we delve into the current state of viniculture in the country, we’ll explore the causes behind the declines in output, the economic ramifications for winegrowers, and the growing movement among winemakers advocating for more robust support and sustainable practices. Encompassing everything from environmental challenges to the urgent calls for policy change, the future of French wine production hangs in the balance.
Impact of Climate Change on French Wine Production
Climate change has emerged as a pervasive challenge for the French wine industry, significantly skewing production expectations for the years to come. The dramatic shifts in weather patterns have produced not only heatwaves but also unpredictable drought conditions, which have severely impacted grape yields. In recent years, many regions, particularly in southern France, have witnessed substantial reductions in their harvests. With the 2025 wine harvest paralleling that of 2024, it becomes evident that climate fluctuations are a primary contributor to the ongoing decline in wine output. Winegrowers express their concerns over the sustainability of their practices in the face of these changing climate conditions.
The repercussions of these climate changes extend beyond mere production numbers. French wine producers, especially those in areas like Aude, are now grappling with the psychological toll of consecutive poor harvests, creating an atmosphere of uncertainty among vintners. The heatwaves have turned what used to be reliable harvest seasons into periods of anxiety and despair. As they respond to climate challenges, winemakers are increasingly motivated to explore innovative methods such as drought-resistant grape varieties, yet the industry remains at the mercy of nature’s unpredictability.
Challenges Faced by French Winegrowers
French winegrowers are currently navigating a perilous landscape fraught with challenges stemming from various socio-economic factors and their own production woes. The aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic has not only disrupted traditional supply chains but has also altered consumer preferences, pushing many to prioritize value over tradition. Adding to the struggle, the sector has erupted into protests, echoing the frustrations of growers like Jérôme Despey, who highlight the pressing need for better governmental support. As these vintners voice their discontent, they are not merely lamenting a bad harvest; they are fighting for the survival of an industry that is increasingly cornered by both climate crises and rising operational costs.
Furthermore, the pricing pressures from international wine markets pose a formidable challenge for local producers. The influx of cheaper imports has compounded domestic struggles, forcing many growers to rethink their strategies in a market that now favors accessibility. In this context, the 2025 wine harvest is not just a benchmark for production metrics, but a litmus test for the resilience of French winegrowers amid increasing global competition. The dialogue surrounding the industry is shifting towards adaptation—whether through strategic innovations or collective action to fortify this storied sector against impending economic and environmental challenges.
The Wine Industry Protests: A Cry for Help
The protests staged by wine producers in southern France serve as a powerful testament to the growing discontent within the industry. On November 15, 2024, thousands of winemakers gathered in Béziers to voice their frustrations over the compounded impacts of climate change, rising costs, and insufficient governmental support. These demonstrations are not mere expressions of anger, but rather, they signify a critical cry for help from a community deeply affected by the declining yields and competitive pressures that have defined the past few years. As the wine industry rallies to address these challenges, the need for solidarity among growers becomes ever more vital.
Amid these protests, it is clear that the industry is not fighting alone; public sentiment is increasingly resounding in support of local winegrowers, as consumers begin to recognize the significance of preserving local vineyards. The collective action of the wine community highlights the intricate ties between traditional practices and modern challenges, aiming to secure a future not just for the 2025 wine harvest but for the generations that will continue to cultivate France’s rich vinicultural heritage. By galvanizing public and government attention, these protests serve as a crucial catalyst for potential policy changes that could significantly impact the resilience of French wine production.
Future Outlook for the French Wine Sector
Looking ahead, the future of the French wine sector appears precarious amid ongoing climate disruptions and changing market dynamics. While the 2025 harvest is set to mirror that of the dismal 2024 output, experts suggest that proactive adaptations may pave the way for recovery. Innovations in vineyard management, such as better water conservation techniques and selecting climate-resilient grape varieties, could potentially mitigate some adverse effects of climate change. However, such adaptations demand significant investment and a restructuring of current practices, which will take time and resources that many growers may not yet possess.
In parallel, the French wine industry is contemplating the need for a renaissance—one that not only respects traditional viticulture but embraces modern environmental practices. This strategic pivot could offer a more sustainable path forward, helping to alleviate the ongoing complaints surrounding insufficient governmental support. As the sector struggles through its current turmoil, the necessity for a united front among French winegrowers becomes critically evident. Collaborations across the industry can amplify voices demanding necessary reforms, ensuring that the legacy of French wine production continues to thrive despite the myriad challenges on the horizon.
Adapting to Market Shifts: French Wine Innovation
As the landscape of the wine industry evolves, French winegrowers are increasingly required to pivot and adapt to new market realities. The consumer shift towards sustainable and organic products has opened doors for innovation within the sector. Winegrowers are responding by exploring techniques such as organic farming, minimal intervention winemaking, and sustainable practices that not only appeal to environmentally conscious consumers but also safeguard their own futures against climate vagaries. This trend is pivotal as demand changes, positioning French wines to reclaim a competitive advantage amidst rising international influences.
Furthermore, an increased focus on marketing strategies that highlight the terroir attributes and heritage of French wines can play a crucial role in attracting a new generation of consumers. By harnessing digital platforms and direct-to-consumer sales channels, winegrowers can enhance their visibility and foster a deeper connection with wine enthusiasts. Ultimately, as the French wine industry grapples with declining outputs and pressures from international markets, innovation and adaptation will be key drivers for securing a sustainable future, securing not just the 2025 wine harvest but ensuring the longevity of the tradition itself.
Government Support and Policy Changes for Winegrowers
The need for robust government support has never been clearer for French winegrowers, as they navigate the tumultuous waters brought on by climate change and economic pressures. Many producers are calling for policies that address the specific challenges facing the sector, such as subsidies for sustainable farming practices and assistance in mitigating losses from natural disasters. Increased financial support could empower growers to invest in necessary innovations that enhance resilience and sustainability, essential for adapting to both current and future challenges. Furthermore, diplomatic efforts to protect local markets from the influx of cheap international wines are pivotal to maintaining fair competition.
In addition, the role of policy changes extends beyond immediate financial aid; there is a crucial need for comprehensive strategies that foster education and research within the wine sector. By investing in advancements that address climate change impacts on wine production, the government can play a significant role in shaping the future of French wine. Such initiatives would not only stabilize the industry through uncertainty but also position France as a leader in global sustainable wine production. As protests from winegrowers highlight urgent demands, lawmakers are urged to engage meaningfully with the sector, ensuring that the policies implemented resonate with the unique needs of the producers.
Climate Adaptation Strategies in the Vineyards
As the effects of climate change become more pronounced, French winegrowers are increasingly adopting a range of strategies to adapt their vineyards to shifting conditions. Drought-resistant grape varieties are becoming more prevalent, allowing producers to withstand the harsh realities posed by rising temperatures and inconsistent rainfall patterns. Techniques like cover cropping and advanced irrigation systems are also being introduced to conserve moisture and improve soil health, fostering a more resilient agricultural ecosystem. These adaptive practices not only aim to improve yields but also enrich the quality of wine, ensuring that it stays true to the distinctive terroir of the region.
Moreover, the emphasis on climate adaptation has opened avenues for collaboration among winegrowers, scientists, and policymakers. This multi-stakeholder approach is crucial in developing innovative solutions tailored to specific regional challenges. Workshops, research endeavors, and shared resources have become vital components of this collaborative landscape, enabling producers to learn from one another and implement best practices. By fostering a community-centric approach to vineyard management, French winegrowers are not only working towards mitigating climate impacts on their harvests but are also securing the fond legacy and future of French wine production.
The Rise of Sustainable Practices in Winemaking
The shift towards sustainability in winemaking is not merely a trend; it is a critical response to the myriad challenges faced by the French wine industry today. As consumers increasingly demand environmentally responsible products, winegrowers are embracing organic and biodynamic practices that enhance the health of their vineyards and ecosystems. This transformation involves reducing chemical inputs, diversifying crops, and improving the overall biodiversity of the vineyard environment, which can lead to more robust grapes and a lower environmental footprint. Proponents of sustainable winemaking argue that these practices are essential not only for the health of the planet but also for the identity of French wines that define their unique flavors and character.
Additionally, the rise of sustainable practices can significantly bolster the economic prospects of winegrowers, opening up new markets and consumer segments that prioritize quality and environmental impact. As these practices become more commonplace, they also contribute positively to the public perception of the French wine industry, garnering respect and admiration from both local and international consumers. Through advocacy and education on the benefits of sustainable winemaking, wine producers are beginning to reshape the narrative around French wine, catalyzing an industry-wide renaissance that could define the future of French wine production amidst emerging global trends.
Market Dynamics: Understanding Global Competition in Wine
In recent years, the global wine industry has witnessed a significant shift in market dynamics, affecting how French wine is positioned internationally. With emerging wine-producing countries entering the market, French producers face heightened competition that challenges their traditional dominance. These countries often offer lower pricing structures, compelling French winegrowers to reassess their value propositions and reconsider pricing strategies. As the market evolves, understanding these dynamics becomes crucial for maintaining competitiveness and securing market share, particularly for the 2025 wine harvest and beyond.
Moreover, adapting to these global market changes requires a multifaceted approach from French winegrowers. This includes enhancing marketing efforts to highlight the quality and distinctiveness of French wines, leveraging heritage, and emphasizing the unique terroirs that define them. Additionally, innovation in both product offerings and distribution methods—such as e-commerce channels—can help local producers expand their reach in an increasingly saturated market. As the competition becomes fierce, the capability of French wine producers to respond and adapt effectively will determine their sustained success in the years to come.
Future Harvest Predictions and Economic Implications
As we look towards future harvests, particularly the anticipated outcomes for 2025, predictions suggest continued challenges for French wine production. With climate change effects persisting and the demand for wine changing, winegrowers may face an uphill battle to achieve gains in yield and quality. Economic implications of these forecasted harvests are significant; lower production rates often correlate with higher pricing, impacting both consumers and producers. As winemakers adjust to these realities, understanding market trends and consumer behavior will be integral to navigating these economic challenges.
However, there is a silver lining amidst the uncertainty. With the increasing focus on quality over quantity in the wine industry, many French producers have the opportunity to position themselves as premium wine brands. By investing in quality grapes, sustainable practices, and storytelling around their wine heritage, producers can capture a niche market that values artisanal craftsmanship rather than mass production. The economic outlook may hinge on such strategic pivots, as the world’s wine consumers increasingly seek authenticity—suggesting that hard-hit winegrowers might be able to turn adversity into opportunity as they prepare for the uncertain harvests ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What impact is climate change having on French wine production?
Climate change is having a profound impact on French wine production, particularly evident in the 2025 wine harvest, which is projected to be similar to the disastrous yields of 2024. Drought and heatwaves have led to reduced grape yields, with some regions experiencing consecutive small harvests, significantly affecting overall production.
What challenges are French winegrowers facing due to the declining wine production?
French winegrowers are grappling with numerous challenges, including climate change effects like prolonged droughts and heatwaves, which have contributed to wine production decline. Additionally, lack of adequate government support and competitive pressures from international markets exacerbate their difficulties, prompting protests among producers.
How has the 2025 wine harvest been affected by recent weather patterns in France?
The 2025 wine harvest in France has been severely affected by adverse weather patterns, particularly due to heatwaves. As a result, the expected grape yield stands at approximately 36.2 million hectoliters, mirroring the disappointing figures observed in 2024, leading to ongoing concerns among French winegrowers.
What are the main factors contributing to the decline in French wine production?
The decline in French wine production is largely attributed to climate change, which has led to diminished harvests over the past few years. Factors include recurrent droughts, heatwaves, inadequate government support for winegrowers, and intensifying competition from global wine markets, all contributing to the industry’s challenges.
Why did French wine industry protests erupt in 2023?
Protests in the French wine industry erupted in 2023 due to widespread grievances among winegrowers regarding the challenges posed by climate change and the resulting decline in wine production. Producers are frustrated by insufficient government assistance, competitive pricing pressures, and the cumulative impact of consecutive poor harvests.
What actions are French winegrowers taking to address the challenges of wine production decline?
In response to the challenges of wine production decline, French winegrowers are increasingly voicing their concerns through protests and advocating for better government support. Additionally, many are exploring sustainable agricultural practices to adapt to climate change and improve resilience in the face of ongoing market pressures.
How is international competition affecting French wine production?
International competition is negatively impacting French wine production by driving prices down and shifting consumer preferences towards global wine options. This intensifies the struggles of French winegrowers, already grappling with a decline in production due to climate challenges, by forcing them to compete with lower-priced wines from abroad.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Production Estimates | In 2025, French wine production is expected to match the disappointing levels of 2024, with an estimated yield of 36.2 million hectoliters. |
| Impact of Climate Change | The wine sector is facing consecutive years of drought and heat waves, leading to significantly reduced harvests in regions like Aude, dropping from 3.9 million to 2 million hectoliters. |
| Economic Pressures | Winegrowers face inadequate government support and intense pricing pressures from international markets, contributing to their distress. |
| Winegrowers’ Response | Major protests erupted among producers in southern France over their grievances, highlighting the increasing frustrations within the sector. |
Summary
French wine production is currently facing significant challenges as it struggles to recover from the impacts of climate change and economic pressures. The ongoing difficulties in achieving sustainable yields, coupled with competitive forces from international markets, require urgent attention and supportive measures for winegrowers. As we move into 2025, the hope for revitalizing the French wine sector appears bleak, necessitating strategic actions to safeguard this integral part of France’s cultural and economic heritage.