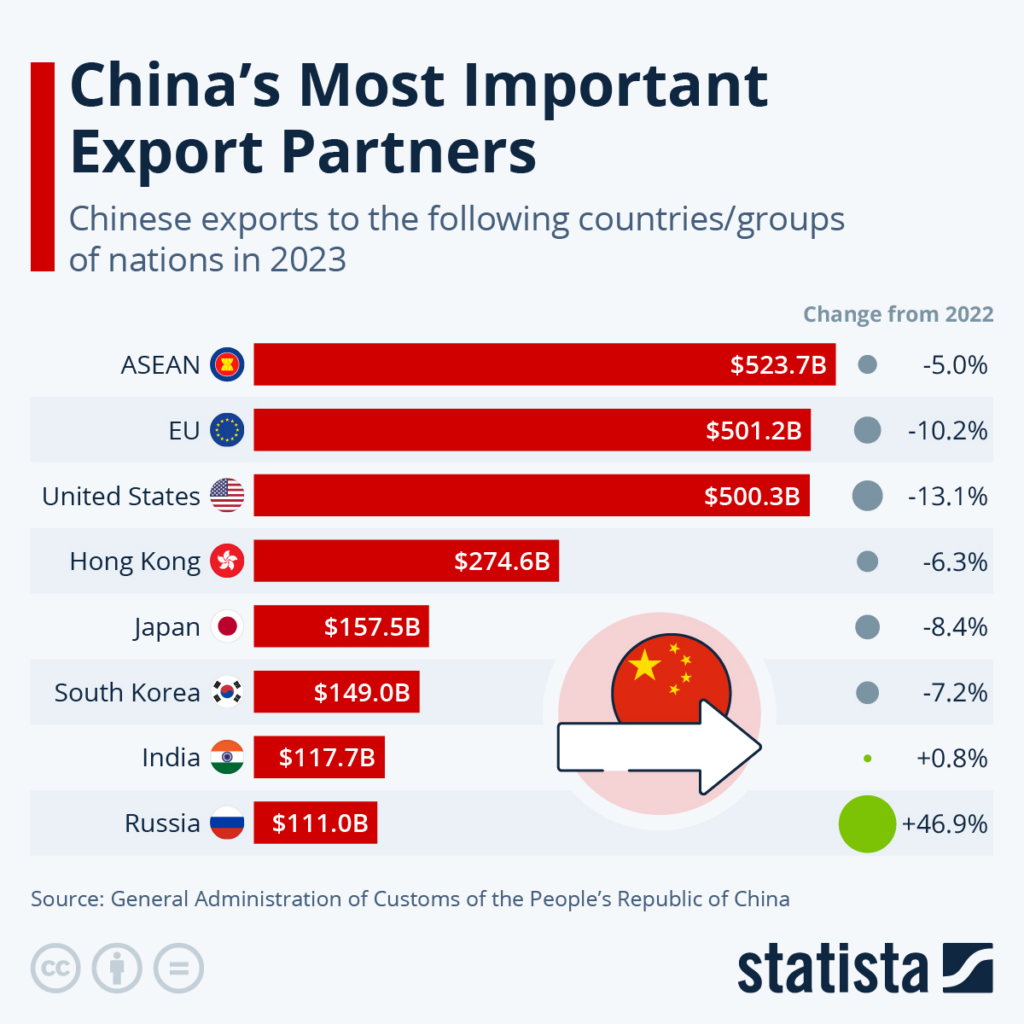
Chinese exports have become a focal point of global trade dynamics, especially as the country navigates a complex economic landscape. Despite a notable decline in exports to the US, China’s trade surplus has astonishingly surpassed $1 trillion for the first time, highlighting its significant role in international markets. This growth indicates that while exports to the US may falter, other regions continue to eagerly receive Chinese goods. The recent statistics, which reveal a 5.9% increase in exports in November compared to the previous year, underscore the rise of China’s export growth amidst EU concerns about a potential market flood. As nations like France consider implementing protective tariffs on Chinese products, the conversation around China’s trade practices and their global impact intensifies.
In recent years, the international marketplace has faced an influx of goods originating from China, marking a transformative period in global commerce. While scrutiny regarding America’s diminishing imports from the Asian powerhouse grows, European nations express apprehension about the overwhelming volume of products being exported from China. The remarkable trade balance, boasting a surplus exceeding $1 trillion, reflects China’s aggressive pursuit of new markets amid modest domestic demand. Reports indicating a 5.9% escalation in export figures suggest a robust manufacturing sector aiming to leverage alternative markets in response to evolving geopolitical tensions. As lawmakers consider measures against imported Chinese goods, the dialogue surrounding international trade practices remains more vital than ever.
Impact of China’s Trade Surplus on Global Markets
China’s trade surplus, which has now surpassed $1 trillion, represents a significant shift in the global economic landscape. This milestone highlights the country’s ability to export more than it imports, leading to increased scrutiny from international trading partners, particularly in Europe and the United States. The continuous growth of Chinese exports is indicative of the country’s expansive manufacturing capabilities and its strategy to seek out new markets as domestic demand wanes. As a result, the implications of this surplus extend beyond mere statistics; they impact global supply chains, pricing strategies, and foreign trade policies.
Moreover, a rising trade surplus can provoke reactions from other economies that may feel threatened by China’s economic dominance. The EU’s concerns regarding this surge have prompted dialogues among member states about potential countermeasures. Many European leaders, including President Macron, fear that unless China addresses these trade imbalances, they may have to implement tariffs similar to those seen in the US. Such actions could escalate trade tensions, ultimately affecting not only Chinese exports but also global markets dependent on Chinese goods.
Chinese Export Growth Amid Global Trade Tensions
Despite facing a decline in exports to the US, China’s overall export growth has remained robust, with an increase of 5.9% noted in November. This growth reflects China’s strategic pivot to other regions, seeking to offset vulnerabilities in its trading relationship with the US. Key markets in Asia, Africa, and Latin America have shown greater receptivity to Chinese products, highlighting a shift in global trade dynamics. This diversification strategy allows China to mitigate risks associated with the volatility of any single market, particularly as the US continues to impose tariffs on various Chinese goods.
The resilience of Chinese exports even during periods of trade tension indicates the country’s formidable manufacturing and technological capabilities. However, the decline in exports to the US underscores the complexities of international trade relationships. As tariffs and trade policies continue to evolve, China’s export sector must adapt swiftly. The combination of economic growth in emerging markets and declining relations with traditional partners such as the US exemplifies the challenges and adaptations that China faces in maintaining its export growth trajectory.
EU Concerns Over Increasing Chinese Exports
European nations have voiced rising concerns about the rapid growth of Chinese exports and how it threatens their own manufacturing industries. The stark figures revealing China’s trade surplus have intensified calls for scrutiny on the import of Chinese goods and potential protective measures. European leaders worry that without intervention, their economies might suffer from what they view as unfair competition fueled by subsidized Chinese products. This concern was palpable during French President Macron’s recent discussions with Chinese officials, where he articulated the potential consequences of ignoring European apprehensions.
The EU’s focus on addressing these burgeoning concerns signifies a shift towards a more proactive stance in international trade negotiations. As discussions among EU members continue, the possibility of introducing tariffs on Chinese imports looms large. Such measures, similar to those enacted by the US, could reshape the trade relationship between China and Europe, creating a more level playing field, albeit at the risk of escalating trade hostilities. The challenge for Europe will lie in balancing economic growth while protecting local industries against a backdrop of increasing global competition.
Tariffs on Chinese Products: A Necessary Measure?
The application of tariffs on Chinese products has become a hot topic in recent years, especially with the growing trade imbalance noted in various reports. As countries like the US have taken drastic steps to impose higher tariffs in response to perceived unfair trade practices, policymakers in Europe are contemplating similar strategies. France’s President Macron has urged the EU to take firm action, suggesting that without meaningful responses to the surge in Chinese exports, European industries may suffer losses that could be detrimental to the economy.
Implementing tariffs on Chinese goods, however, is not without its challenges. While such measures could protect local industries in the short term, they may also lead to retaliation from China, creating a tit-for-tat scenario that could escalate trade tensions globally. Moreover, increased costs for imported goods could ultimately affect consumers and businesses that rely on affordable Chinese products. Therefore, as the EU navigates this complex situation, careful consideration must be given to the potential ramifications of enacting tariffs on Chinese exports.
The Future of Chinese Exports in a Shifting Global Economy
As we look to the future, the landscape of Chinese exports is expected to change significantly in response to global economic shifts. The rising trade surplus reflects not just a strength in manufacturing but also China’s efforts to penetrate new markets and diversify its export destinations. However, it is important to recognize that external pressures, such as tariffs and geopolitical tensions, will continue to shape the trajectory of China’s export growth. The ongoing trade discussions, particularly with Western nations, will play a crucial role in determining how China adapts its strategies.
Furthermore, the strategic move towards e-commerce and technology-driven exports is likely to redefine what Chinese goods look like in global markets. China has been increasingly investing in innovation and technology to enhance the value of its exports, beyond traditional manufacturing. This shift could enable the nation to maintain robust growth despite potential barriers imposed by trading partners. As countries across the globe reevaluate their trade policies, China’s ability to innovate will be a key determinant of its sustained export success and its role in the international economy.
Challenges to China’s Export Growth from Economic Policies
The landscape of international trade is fraught with challenges posed by varying economic policies across nations. As China continues to navigate between maintaining its strong export capabilities and addressing external pressures, there are significant hurdles to overcome. Economic policies, particularly those targeting industries that have become overly reliant on exports, create an environment of uncertainty. This is particularly relevant in the context of tariffs on Chinese products, which can disrupt established supply chains and impact pricing structures.
Furthermore, China’s efforts to foster innovation while dealing with declining exports to traditional markets, such as the US, require a careful recalibration of its trade strategies. The challenge lies in fostering growth in sectors where domestic consumption is sluggish, while simultaneously mitigating the negative impacts of protectionist measures from abroad. By establishing new partnerships and exploring alternative markets, China aims to cushion the effects of these economic policies on its expansive export sector and maintain its position as a leading global exporter.
The Role of Emerging Markets in Chinese Export Strategy
Emerging markets play an increasingly vital role in China’s export strategy as the nation seeks to offset declines in traditional markets like the US. As China’s domestic demand continues to fluctuate, looking toward regions such as Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America allows for sustaining growth in export volumes. These emerging economies often welcome Chinese investments and exports, creating a mutually beneficial relationship that encourages economic development and trade diversification.
In addition, the growth of e-commerce and digital trade channels presents new opportunities for Chinese exports in these regions. China’s technological prowess in online platforms facilitates access to markets that may have previously been challenging. As logistics and infrastructure improvements continue across these developing nations, the potential for expanding Chinese exports grows, reinforcing China’s strategic pivot away from reliance on traditional Western markets. In essence, the robust growth in emerging markets could be a fundamental pillar supporting China’s future export ambitions.
Adapting to Global Trade Trends: China’s Response
As global trade dynamics evolve, China faces the pressing need to adapt its strategies to maintain a competitive edge in exports. The fluctuations in trade relationships, particularly with the US and EU nations, require China to be agile and proactive in its approach. Understanding and responding to the concerns of other nations regarding trade imbalance is crucial for fostering healthier trade relations. By addressing these issues head-on, China can mitigate the risks of economic isolation and tariffs that threaten its export growth.
Furthermore, by embracing innovation and shifting towards higher value-added products, China can improve its standing in the global market. This transition not only enhances the quality of Chinese exports but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and ethically produced goods. China’s response to global trade trends must encompass both a commitment to high-quality exports and a recognition of the necessity for transparent trade practices. By taking these steps, China can continue to forge strong partnerships while bolstering its economic resilience against external pressures.
The Importance of Trade Relations in Sustaining Export Growth
Trade relations are fundamental to sustaining and enhancing China’s export growth in a rapidly changing global marketplace. With various nations imposing tariffs on Chinese products and expressing concerns over trade imbalances, it is imperative that China cultivates strong diplomatic ties. By engaging in fruitful negotiations and reinforcing trade partnerships, China can both alleviate pressures on its exports and create opportunities for collaboration in various sectors. The importance of maintaining positive trade relations cannot be overstated, as these ties will ultimately shape the future trajectory of Chinese exports.
Moreover, engaging in multinational forums and discussions serves as a platform for China to advocate for fair trade practices while addressing concerns raised by trading partners. By participating in dialogue, China can demonstrate its commitment to cooperation and reciprocity. Strengthening trade relations also opens the door to potential trade agreements that could mitigate tariff impacts and fortify access to crucial markets. As China navigates these complex relationships, the emphasis on diplomacy in international trade will be essential for fostering long-term growth in its export sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors are contributing to China’s trade surplus despite the decline in exports to the US?
China’s trade surplus has reached over $1 trillion, driven by a 5.9% growth in exports in November while imports rose only 1.9%. This indicates a significant difference between China’s output and domestic demand, propelling the country to seek new markets for its products globally.
How are EU concerns about China impacting trade relationships with Chinese exports?
EU concerns regarding a surge in Chinese exports are increasing pressure on trade relationships. European leaders fear that without measures against China, such as tariffs on Chinese products, the EU could suffer from an influx of competing goods. This has been a point of discussion, exemplified by French President Macron’s visit to China.
Why did the US impose tariffs on Chinese products, and what effect has this had on Chinese exports?
The US imposed tariffs on Chinese products to combat what it sees as unfair trade practices and an imbalance created by China’s growing trade surplus. While exports to the US have declined, China has continued to increase its exports to other regions, highlighting its reliance on markets outside the US.
What are the implications of China’s export growth on global market dynamics?
China’s robust export growth, evidenced by increased shipments despite declining exports to the US, alters global market dynamics by introducing competitive pricing and availability of goods. This can lead to increased tensions with other economies, particularly in the EU, which are concerned about maintaining their market share.
How could future tariffs on Chinese exports affect global trade?
Future tariffs on Chinese exports could lead to retaliatory measures from China, affecting global trade networks. This may result in increased prices for consumers in importing countries and alter trade routes, pushing countries to diversify their supplier bases away from China.
| Metrics | Value | Comparative Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Chinese Trade Surplus | Exceeds $1 trillion (€860 billion) | |
| Chinese Exports Growth (November) | 5.9% | Compared to previous year, imports rose by only 1.9%. |
| EU Concerns | Growing Chinese exports | Concerns voiced by President Macron and echoed by US officials on tariffs. |
Summary
Chinese exports continue to significantly impact global trade dynamics despite the recent decline in exports to the US. Over the past year, China has recorded a historic trade surplus, signaling persistent demand for its products in various global markets. This trend raises concerns among European nations, prompting political discussions about potential measures to address the implications of increasing Chinese exports on local economies. As countries assess their response to this economic shift, the conversation around tariffs and trade policy becomes more critical.