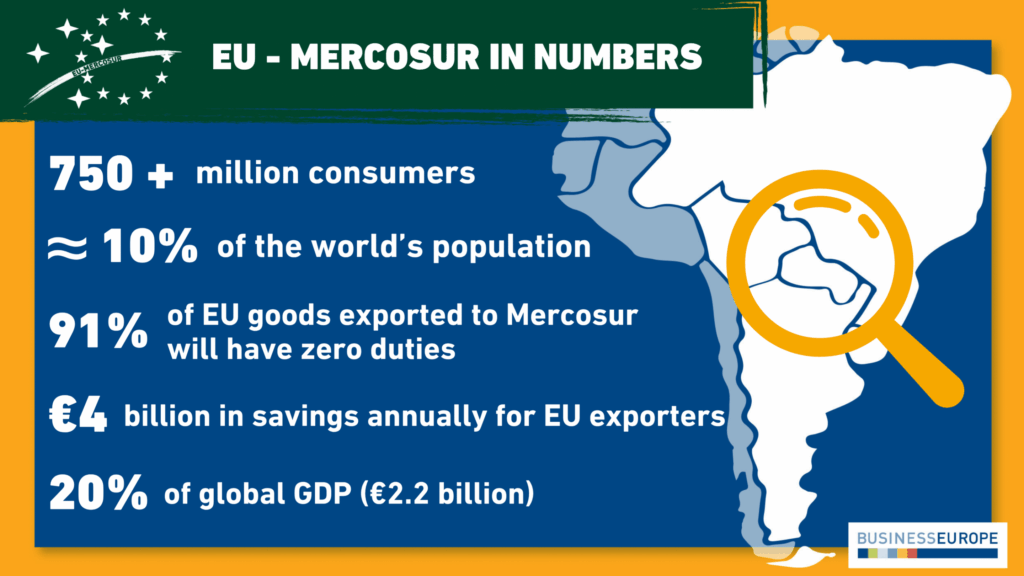
The EU-Mercosur trade agreement represents a significant opportunity for economic growth, uniting Europe and South America under a single free trade framework. This deal, potentially linking 750 million consumers, has been a focal point in discussions surrounding EU trade deals, especially given the economic challenges posed by France’s public finances. As President Emmanuel Macron navigates rising tensions within the agricultural sector regarding this agreement, the stakes for industries reliant on export markets could not be higher. With French farmers voicing strong opposition to increased competition from the Mercosur bloc, the future of this deal is becoming increasingly precarious. Thus, the EU-Mercosur trade agreement not only highlights trade ambition but also exposes the delicate balance of national interests amidst broader economic aspirations.
The trade pact between the European Union and the South American trading bloc, Mercosur, stands as a bold initiative aimed at enhancing intercontinental trade relations. Known for its potential to create a vast market opportunity, this agreement is crucial as economies look to rebound post-pandemic. The complex dynamics, particularly in France where public sentiment around agriculture is strong, showcase the challenges in negotiating such expansive free trade agreements. As key players like Emmanuel Macron weigh the pros and cons, the implications for both domestic stability and international cooperation are profound. This multifaceted trade dialogue not only reflects on EU-Mercosur’s potential benefits but also highlights the nuanced negotiations essential for its success.
Overview of France’s Public Finances and Economic Challenges
France’s public finances are under considerable pressure, grappling with rising debts and an urgent need for fiscal reforms. Under President Emmanuel Macron’s leadership, the focus has shifted to balancing austerity with economic growth. The French government aims to reduce the budget deficit while still investing in critical areas such as infrastructure and healthcare. However, mounting public dissatisfaction over cost-cutting measures poses a significant challenge, bringing the need for effective governance and transparent fiscal policies to the forefront.
One of the core challenges facing France’s public finances is the delicate balance between taxation and welfare. As the government looks to optimize tax revenues, it often clashes with public expectations for social services. Macron’s administration has attempted to streamline public spending, but this has frequently been met with protests, exemplifying the tension between economic policy and public sentiment. In navigating these fiscal intricacies, France must ensure that its economic strategies align with the population’s demands for financial security and social equity.
The Significance of the EU-Mercosur Trade Agreement
The EU-Mercosur trade agreement represents a monumental step towards creating one of the world’s largest free trade areas, linking the European Union with the Mercosur bloc of South America, which includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. This agreement is designed to enhance trade relations, reduce tariffs, and foster economic integration between these regions. Its potential benefits include increased market access for European businesses and the opportunity to diversify import sources, particularly in agriculture and sustainable goods.
However, the agreement has faced significant backlash within France, where agricultural interests express concerns about competition from Mercosur countries. The fear is that cheaper imports might undermine local farmers already struggling with production costs. Amidst this, President Emmanuel Macron’s plea for a postponement of the agreement highlights the complexity of political pressures and economic realities involved in such a substantial trade deal. Balancing France’s agricultural needs with the broader European objectives of securing enhanced trade ties remains a crucial task as negotiations progress.
Emmanuel Macron’s Leadership and Trade Policies
Under Emmanuel Macron, France’s approach to international trade has undergone a notable transformation, with a drive towards expansive free trade agreements while simultaneously safeguarding national interests. Macron champions open markets as a means to stimulate economic growth and job creation, viewing the EU-Mercosur trade agreement as a pivotal component of this strategy. His government has sought to position France as a progressive player in global commerce, but this vision has to contend with domestic resistance, particularly from rural constituencies wary of foreign competition.
Macron’s leadership style emphasizes negotiation and compromise, and he has consistently advocated for a balanced approach in EU trade deals. Nevertheless, the rising protectionist sentiments across Europe challenge this outlook, pressuring him to reconsider the implications of opening up markets. The delicate interplay of fostering international partnerships while maintaining public confidence in the government’s economic stewardship represents a significant test for Macron as he navigates France’s future in the global economy.
Impacts of EU Trade Deals on France’s Economy
The implications of EU trade deals, including the EU-Mercosur agreement, on France’s economy are multifaceted. On one hand, these agreements promise expanded export opportunities for French industries, particularly in the automotive and pharmaceutical sectors, which could lead to increased employment and economic rejuvenation. On the other hand, concerns persist regarding the potential influx of imports from South America, which could pose risks to local producers, particularly in agriculture.
Furthermore, the ramifications of these trade deals extend to various sectors of the economy, influencing everything from consumer prices to job security within local markets. France’s government is tasked with finding a middle ground that embraces the benefits of trade liberalization while instituting protective measures for vulnerable domestic industries. As the balance of globalization and local economic health is continually scrutinized, the French public’s response will play a pivotal role in shaping future trade policies.
The Role of French Agriculture in Trade Discussions
French agriculture holds a significant position in discussions surrounding trade agreements such as EU-Mercosur. Farmers and agricultural groups have voiced strong concerns about the potential negative impacts of foreign competition resulting from such agreements. They argue that increased importation of agricultural goods from South America could compromise local food production standards and threaten the livelihoods of French farmers who rely on the local market.
In response to these worries, the French government has faced mounting pressure to ensure that any trade deals incorporate safeguards for the domestic agricultural sector. Negotiations surrounding the EU-Mercosur agreement reflect a broader conflict between the aspirations of liberalizing trade and the imperative of protecting France’s agricultural heritage. Moving forward, the government’s challenge will be to strike a balance that addresses these concerns while capitalizing on the benefits that broader trade relationships offer.
Public Response to Trade Agreements and Farming Issues
The public response to the proposed EU-Mercosur trade agreement reveals deep divisions within French society, particularly among those associated with the agricultural sector. Farmers have mobilized to express their discontent, arguing that the influx of cheaper agricultural products from the Mercosur bloc threatens not only their economic survival but also the environmental and quality standards associated with French produce. This grassroots resistance underscores the importance of public opinion in shaping trade negotiations.
Moreover, as France prepares for upcoming elections, the sentiments of voters in rural areas are crucial. Political narratives surrounding the EU-Mercosur agreement will likely play a significant role in influencing electoral outcomes, as candidates align their platforms to address the concerns of constituents. Whether through protests or political discourse, public engagement on these issues signals a critical juncture for Macron’s administration, necessitating a thoughtful approach in reconciling trade ambitions with the realities faced by everyday citizens.
Navigating Political Challenges in Trade Policy
France’s political landscape surrounding trade policies, especially in the context of the EU-Mercosur deal, is fraught with challenges. The government must navigate a complex web of interests, minimizing backlash from both agricultural factions and industrial proponents of liberalized trade. Macron’s call for a review of the agreement exemplifies the political sensitivity surrounding such negotiations, indicating a willingness to adapt policy in response to public sentiment.
With political parties from various spectrums weighing in on the trade agreement, the discussions reflect broader ideological conflicts about globalization and its impact on national identity. As negotiations progress, France’s ability to reconcile these competing interests will be crucial in determining not only the fate of the EU-Mercosur agreement but also the future of France’s role in global trade dynamics.
The Future of EU Trade Relations and France’s Position
Looking ahead, France’s position in the evolving landscape of EU trade relations will depend on how effectively it addresses both domestic and international pressures. The EU-Mercosur deal could set a precedent for future agreements, potentially influencing how other trade relationships evolve within Europe. France must approach these negotiations with a keen sense of its agricultural interests while still pursuing the beneficent elements of international trade.
As global markets continue to shift, France has an opportunity to position itself as a leader in ethical trade practices that prioritize sustainability and social responsibility. By championing these values within the scope of trade negotiations, Macron’s administration can aim to foster a more balanced approach, advocating for both economic growth and the safeguarding of domestic industries. The ability to lead in this domain could redefine France’s role on the global stage as a model for integrating trade and environmental stewardship.
Conclusion: Balancing National Interests with Global Trade Goals
In summary, France’s quest to balance national interests with global trade goals is a complex and ongoing endeavor. The EU-Mercosur trade agreement exemplifies the challenges faced by the French government in negotiating favorable terms while also responding to strong opposition from the agricultural community. The implications of this agreement will have far-reaching effects, not just on France, but on the entire EU’s trade landscape.
As Macron’s administration navigates this intricate web of interests, the outcome will likely depend on their ability to engage in meaningful dialogue with all stakeholders involved. By fostering cooperation rather than conflict, France can aspire to create trade policies that not only bolster the economy but also respect the social fabric of the nation, strengthening its position in an ever-complicated global trade environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the EU-Mercosur trade agreement and why is it significant for France?
The EU-Mercosur trade agreement is a comprehensive free trade deal between the European Union and the Mercosur bloc, which includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. This agreement is significant for France as it could potentially enhance trade relations and economic opportunities, particularly benefiting the industrial sector. However, it is contentious due to pushback from French farmers who fear increased competition and environmental concerns.
How does Emmanuel Macron view the EU-Mercosur trade agreement?
Emmanuel Macron has expressed reservations about the EU-Mercosur trade agreement, calling for a postponement of its review. His stance reflects concerns from the agricultural sector in France, which fears adverse effects on local farming due to increased imports from Mercosur countries. Macron’s position seeks to balance international trade benefits with domestic agricultural interests.
What are the implications of the EU-Mercosur trade agreement for France’s public finances?
The EU-Mercosur trade agreement could have mixed implications for France’s public finances. While increased trade may stimulate economic growth and expand tax revenues, the introduction of cheaper agricultural products could place pressure on local farming subsidies and public expenditures aimed at supporting the agricultural sector. Thus, careful assessments are essential to gauge the financial impact.
How do EU trade deals, like the EU-Mercosur agreement, affect local economies in France?
EU trade deals, including the EU-Mercosur agreement, can significantly impact local economies in France. They typically aim to open markets and increase competition, which can lead to lower prices for consumers. However, this can also challenge local producers, particularly in sectors like agriculture, where French farmers worry about competition from imports, potentially leading to economic displacement.
What are the current challenges facing the EU-Mercosur trade agreement negotiations?
Current challenges facing the EU-Mercosur trade agreement negotiations include resurgent opposition from French farmers, concerns regarding environmental standards, and political pressure within EU member states. Additionally, specific incidents, like the outbreak of contagious diseases affecting livestock in France, further complicate support for the deal within the agricultural community.
How might the EU-Mercosur trade agreement impact France’s agricultural sector?
The EU-Mercosur trade agreement could significantly impact France’s agricultural sector by increasing competition from South American imports, which may be produced at lower costs. While some sectors might benefit from new export markets, many French farmers fear that the influx of cheaper agricultural products could undermine local prices and market viability.
What is the significance of the timeline for the EU-Mercosur trade agreement?
The timeline for the EU-Mercosur trade agreement is significant due to political dynamics and upcoming domestic events, such as local elections in France. Delays or postponements, as advocated by President Macron, could influence negotiations and the overall timeline for implementing the deal, affecting trade relations and economic strategies across the EU.
How does the EU-Mercosur trade agreement relate to broader EU trade policy?
The EU-Mercosur trade agreement is a critical element of the EU’s broader trade policy priorities, aiming to foster international cooperation and economic ties. It reflects the EU’s efforts to create strategic partnerships that enhance trade, promote sustainable practices, and navigate complex geopolitical landscapes, including negotiations with other global trade partners.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Background | For 25 years, the EU and Mercosur nations have attempted to finalize a free trade agreement. |
| Countries Involved | Mercosur includes Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay. |
| Current Status | Negotiations are ongoing, with a potential signing date in December 2024. |
| France’s Position | President Macron has called for a postponement of the review of the agreement. |
| Concerns Raised | French farmers express opposition, citing issues like livestock disease outbreaks. |
| Political Sensitivity | The agreement has caused tensions within French politics, dividing opinions. |
Summary
The EU-Mercosur trade agreement represents a significant step towards creating a free trade relationship between the European Union and four South American countries. Despite years of negotiation, current political dynamics, particularly in France, suggest considerable challenges ahead before its implementation. As shown by President Macron’s call for postponement and the concerns of French farmers, the agreement is not just a matter of trade but also a reflection of deeper agricultural and political sensitivities within the EU. Therefore, the path forward remains complicated and fraught with potential hurdles.